Layer Types
Shape
The shape layer type is the simplest type of layer. It shows the point, path or boundary of the item being retrieved. For example, a shape layer showing vehicle trips will show the paths of the trips while stops will show points for each location the vehicle stops.
There is only a single visualisation parameter which is Colour. This determines the colour the shapes appear on the map.
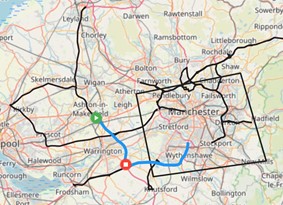
Bubble
The bubble layer is only applicable for point events, that is events which are only a single dot on a map such as a stop or an idle event. It clusters events and shows a bigger dot on the map based on how many events are in the cluster. Hovering on a bubble will show a count of how many events make up the bubble. Clicking on the bubble will zoom the map in to the events that make up the bubble.
There are two visualisation parameters for bubble layers; colour, and distance. Colour determines the colour of the bubbles; while distance determines the size of the bubbles at each zoom level.
In general, the larger the distance parameter the greater the area the bubble uses for clustering points. At closer zoom the distance factor reduces the bubble's catchment area, at far away zoom the distance factor increases it. Distance does correspond to physical distance however because it changes with zoom, there is no way to set or display a fixed distance like 100 metres.
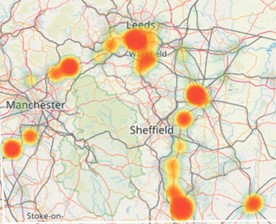
Heat
The heat layer is also only applicable for point events, that is events which are only a single dot on a map such as a stop or an idle event. It clusters events and shows a different colour based on the amount of events in the cluster. It accepts a range of colours between two and ten and colours the areas on the map accordingly. It accepts two additional parameters of blur, which sets the dispersion radius in pixels of each hotspot and radius, which sets the radius in pixels of each cluster.
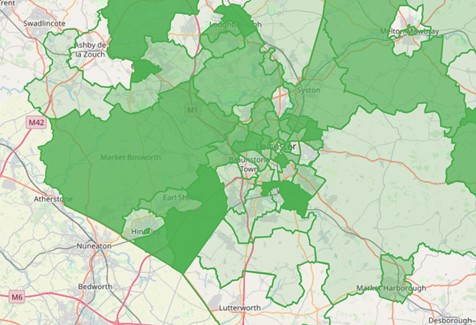
Area
The area layer is a different kind of layer to the others. It’s also known as a choropleth map. It takes an area type as a parameter and colours it according to the chosen source metric. So for example If you choose vehicle time then the area with the most vehicle time will have the darkest colour and the area with the least vehicle time will be the lightest.